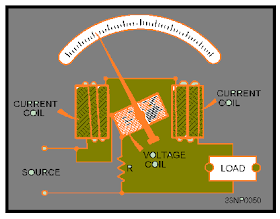
Power is symbolize as (P). It is defined as the amount of energy consumed per unit time. The unit of power is known as theWatt (W). The average power that is absorbed by the load is measured by a wattmeter. Loads consume electric power, converting it to other forms such as mechanical work, heat, light, etc. Examples of loads are electrical appliances, such as light bulbs, electric motors, and electric heaters. When we are using AC, power is determined not only by the r.m.s. values of the voltage and current, but also by the phase angle which will determine the power factor.
ELECTRICITY CONSUMPTION COST
Every appliance we have in our house has its own corresponding power. This power really matters on how much we pay in our electric bills that is why it is important to know how much power present in our appliance. Since we are paying for the electric energy over a period of time, we have to consider how long we use our appliances in our house.
Typical wattages if various appliances:
· Clothes washer = 350–500
· Clothes dryer = 1800–5000
· Fans Ceiling = 65–175
· Window = 55–250
· Furnace = 750
· Whole house = 240–750
· Hair dryer = 1200–1875
· Heater (portable) = 750–1500
· Clothes iron = 1000–1800
· Microwave oven = 750–1100
· Personal computer
· CPU - awake / asleep = 120 / 30 or less
· Monitor - awake / asleep = 150 / 30 or less
· Laptop = 50
· Radio (stereo) = 70–400
· Refrigerator (frost-free, 16 cubic feet) = 725
· Televisions (color)
· 19" = 65–110
· 27" = 113
· 36" = 133
· 53" - 61" Projection = 170
· Flat screen = 120
· Toaster = 800–1400
· VCR/DVD = 17–21 / 20–25
· Vacuum cleaner = 1000–1440
How is energy use of Home Appliances calculated?
Unplug electronic appliances and gadgets when not in use.
When buying new appliances, be sure to purchase energy-efficient
Lessen the hours of using the appliances.
Leave thermostat’s fan switch on “auto”.
Replace light bulbs with CFL’s.
Set the thermostats of the refrigerator at the appropriate temperature.
Clean or replace furnace and air-conditioner filters regularly, following
manufacturer's instructions.
Have self-discipline.
LEARNINGS:
I've learned that the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit time. High energy consumption will result to high electricity bill. I realized that we also need to conserve energy to decrease the quantity of energy used and also, we must use appliances in our house efficiently. Appliances that generate heat contributes high power such as flat iron, rice cooker, and etc.